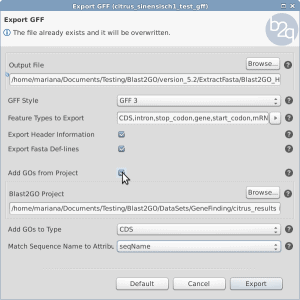
How to export Gene Finder GFF output with GO terms.
This article explains how to export a GFF file with GO terms in Blast2GO.

This article explains how to export a GFF file with GO terms in Blast2GO.
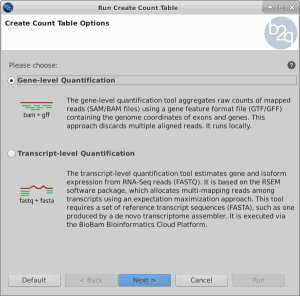
One of the most common applications of RNA-seq is to estimate gene and transcript expression. It starts with the alignment or mapping of reads and there are two possible alternatives: mapping to the genome when a reference sequence is available or mapping to the transcriptome (e.g. de novo assembled transcriptome). Reads may map uniquely or could be multi-mapped reads, while
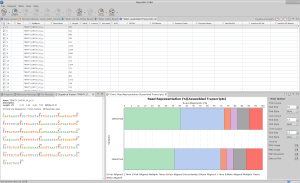
High-throughput sequencing of RNA has revolutionized the study of species for which a reference genome is not available or incomplete by enabling the large-scale analysis of their transcriptomes. While analyses of model organisms generally rely on a reference genome, studies of non-model organisms usually lack this advantage. In the absence of an appropriate reference genome, de novo transcriptome assembly is
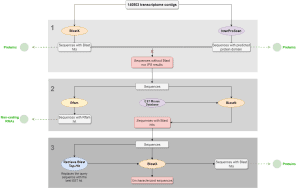
Analysis workflow Objective: To describe the process of a transcriptome characterization using Blast2GO. Input data: A mouse RNA-seq dataset composed of 140803 contigs. Pipeline: Blastx and InterproScan were performed with the complete dataset to identify proteins. Sequences with no Blastx hits nor IPS results were selected and further analyzed. RFAM and Local Blast (against an EST mouse db) were performed with the sequences with
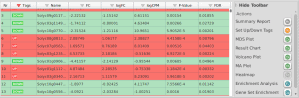
This article explains how to start functional enrichment analysis of pairwise differential genes in Blast2GO.
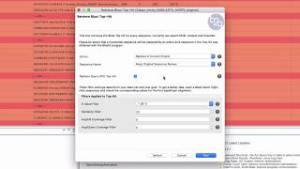
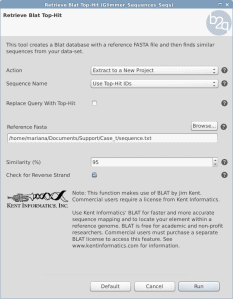
RNA-seq data is sometimes difficult to match with proteins, due to the short length of the reads. When this is the case, it might be useful to try to find EST hits, which can then be used to find new protein matches. In this demo, we will show how to retrieve top EST hits and the different options that this tool
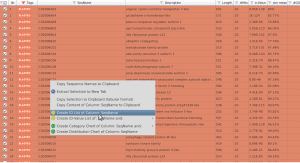
This article explains how to create ID lists of either Blast results or differential expressed genes in Blast2GO.
When running GeneFinding the sequences receive a name with the predicted genes. The first part of the sequence identifier comes from the genome reference sequence name (de-novo assembly) and then a _orfx is appended, where x is a number. Sometimes this name is not useful to proceed with downstream analysis or compare results from other experiments. Is there any way

This video shows an overview of new RNA-Seq features in Blast2GO 5: FastQ Quality Control and Preprocessing, de novo Transcriptome Assembly, Transcript Quantification and Differential Expression Analysis.