De novo transcriptome assemblies are required to analyze RNA-seq data from a species for which there is no reference genome. Once the assembly is complete, researchers need to know how good it is or compare the quality of similar assemblies generated by different parameters. There are several ways to characterize the quality of transcriptome assemblies.
A good metric of assembly quality is evaluating the completeness. This consists of assessing the extent to which the assembly recovers single-copy orthologs that are present across higher taxonomic groups. The expectations for these genes to be found in a genome/transcriptome in single-copy are evolutionarily strong. If they cannot be identified in a transcriptome assembly or annotated gene set, it is possible that the
sequencing and/or assembly and/or annotation approaches have failed to capture the complete expected gene content.
OmicsBox provides the Completeness Assessment functionality, based on BUSCO (Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs). BUSCO determines whether assembly contigs are orthologous with a particular BUSCO dataset, providing quantitative measures of the completeness of transcriptome assemblies. The BUSCO assessment tool implements an open-source Python-based software that employs BLAST+ and HMMER for sequence and profile searches.
OmicsBox offers predefined BUSCO datasets for six major phylogenetic clades:
The Benchmarking Universal Single-Copy Orthologs are ideal for assessing completeness, as the expectations for these genes to be found in a genome/transcriptome in single-copy are evolutionarily strong.
Genes that make up the BUSCO sets for each major lineage are selected from orthologous groups with genes present as single-copy orthologs in at least 90% of species. BUSCO sets were defined using orthologs from OrthoDB.
Running BUSCO in OmicsBox is quite easy. Transcripts sequences must have been previously loaded on the platform. If the RNA-Seq reads have been not assembled yet, we recommend using the RNA-Seq de novo assembly application offered by OmicsBox (based on Trinity). If the transcripts have been previously assembled, they can be loaded into OmicsBox in Fasta format: File -> Load -> Load Sequences -> Load Fasta File.
Configure the BUSCO analysis is simple. Choose the appropriate lineage-specific profile to classify matches, depending on the species to be assessed and set the assessment mode according to the type of sequences to be analyzed (nucleotides or amino-acids).
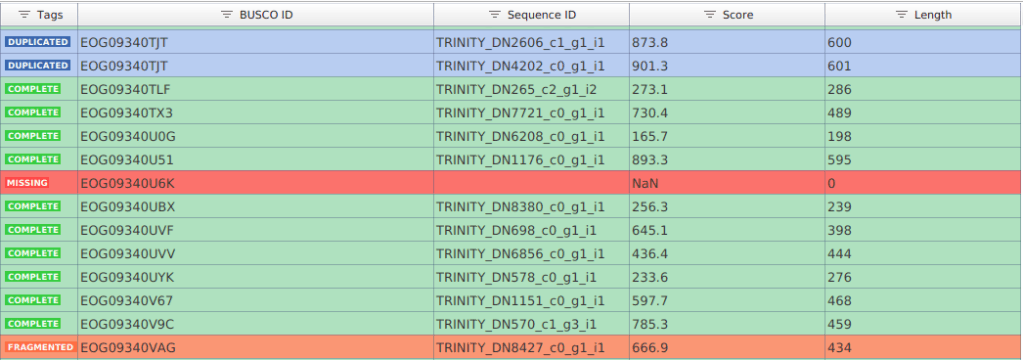
The results are provided in a spreadsheet-style. Each row corresponds to a BUSCO from the lineage database selected, and columns show the following information:
- BUSCO ID: Name of the BUSCO.
- Sequence ID: Name of the transcript/protein sequence matching the BUSCO.
- Score: Score of the alignment.
- Length: Length of the transcript/protein sequence matching the BUSCO.
- Tag: Result category.
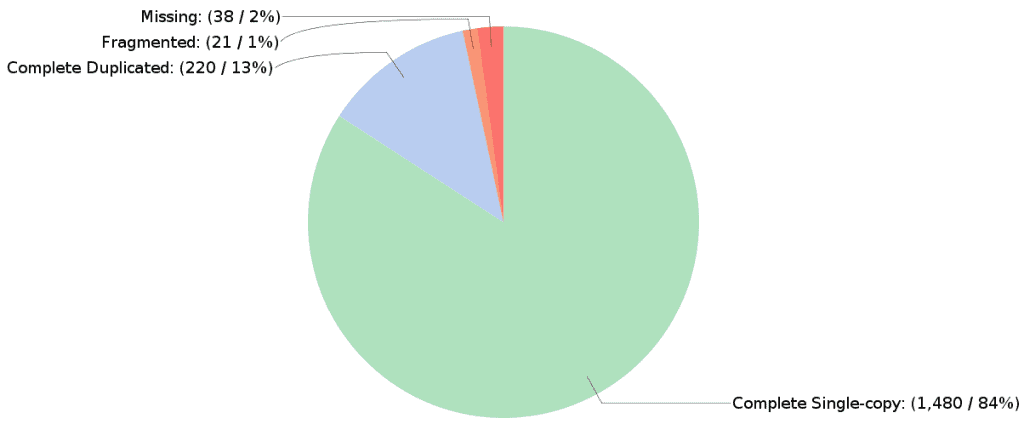
In addition, a result page and a pie chart show a summary of the Completeness Assessment results. The recovered matches are classified as:
- Complete: BUSCO matches have scored within the expected range of scores and within the expected range of length alignments to the BUSCO profile.
- Duplicated: BUSCO matches have been found more than once.
- Fragmented: BUSCO matches have scored within the range of scores but not within the range of length alignments to the BUSCO profile. This indicates incomplete transcripts or gene models.
- Missing: There were either no significant matches at all, or the BUSCO matches scored below the range of scores for the BUSCO profile. This indicates that these orthologues are indeed missing or the transcripts or gene models are so incomplete.
The proportions of BUSCOs found are a good indicator of assembly quality. A high proportion of complete BUSCOs means that the transcriptome of the species under study has been almost completely reconstructed. On the other hand, a high proportion of missing and fragmented BUSCOs suggests that an inadequate assembly strategy was used, or the quality and depth of the sequencing data are not sufficient for this purpose.
Example Use Case
Reanalyzing the A. galli transcriptomic response to an anthelmintic drug with OmicsBox
References
- Completeness Assessment User Manual.
- Simao FA., Waterhouse RM., Ioannidis P., Kriventseva EV. and Zdobnov EM. (2015). BUSCO: assessing genome assembly and annotation completeness with single-copy orthologs. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England), 31(19), 3210-2.
- Kriventseva EV., Kuznetsov D., Tegenfeldt F., Manni M., Dias R., Simao FA. and Zdobnov EM. (2019). OrthoDB v10: sampling the diversity of animal, plant, fungal, protist, bacterial and viral genomes for evolutionary and functional annotations of orthologs. Nucleic acids research, 47(D1), D807-D811.