Introduction
The IsoSeq sequencing method produces full-length transcripts using Single Molecule, Real-Time (SMRT) Sequencing. Long read lengths allow sequencing of full-length transcripts up to 10 kb or longer, removing the need for transcript assembly or inferencing. Therefore, unlike traditional short-read methods, IsoSeq provides a more accurate and complete view of gene expression and alternative splicing events. This comprehensive understanding of transcript diversity enhances our knowledge of gene regulation and cellular processes. Additionally, this tool facilitates the discovery of novel isoforms and gene fusions, expanding our understanding of gene complexity and disease mechanisms.
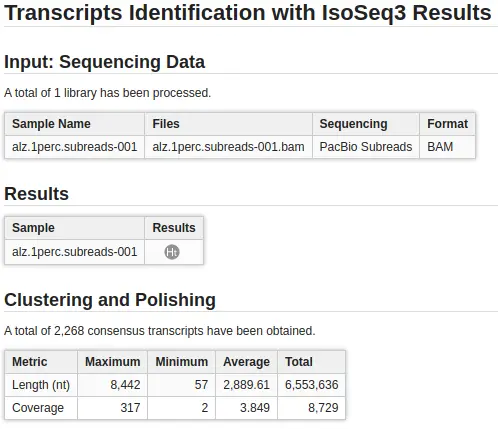
The IsoSeq bioinformatics pipeline processes the data into high-quality consensus transcript sequences that enable accurate isoform annotation and open reading frame prediction. Since OmicsBox 2.0, you can find IsoSeq v3 in the Transcriptomics Module.
Isoform Definition with PacBio Data using IsoSeq
-
IsoSeq accepts PacBio sequencing in the form of subreads and circular consensus sequences (CCS). After providing subreads, the circular consensus sequence calling step performs. Subreads are required in BAM format, while CCS reads can have BAM, FASTA or FASTQ format.
-
The pipeline consists of several steps: CCS calling, demultiplexing, and primer removal, refining, clustering, and polishing. The configuration wizard allows adjusting parameters for each step:
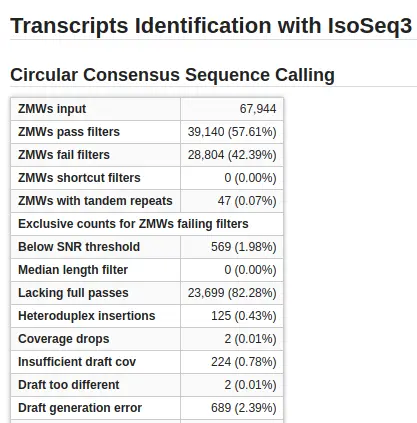
- CCS Calling. In this step, IsoSeq generates a representative circular consensus sequence (CCS) from similar subreads. CCS is This step is only applied if the input was PacBio Subreads.
- Demultiplexing and Primer Removal. Demultiplexing refers to the process of separating or assigning sequencing reads to their respective barcodes. After clusters are done, primers must be removed.
- Refine. It consists of trimming poly-A tails and concatemer removal.
- Clustering. PacBio consensus long reads are mapped among themselves in order to cluster them and find a transcript consensus for each merged cluster.
- Polishing (optional). Each transcript consensus sequence can be improved by generating per-base Quality Values. Note that this step is very time-consuming, and it can only be applied if all input libraries are subreads.
References
IsoSeq v3. Scalable De Novo Isoform Discovery. Töpfer, A. and Tseng, E. 2020. https://github.com/PacificBiosciences/IsoSeq
Useful Links
About the Author
With a biological and technological academic background, including a BSc in Biotechnology and an MSc in Bioinformatics, Enrique’s expertise lies in the areas of Long Reads and Genetic Variation.